Nvidia has been making progress in a technical wall in GPU design wherein it would no longer be capable of shoving more transistors into a GPU die to increase performance to which rate customers have grown accustomed to. GPUs in general are designed as monolithic dies with their functionality under one` roof’. This tends to take place often and the earlier GPUs on some occasion utilised separate chips for specific functionality.
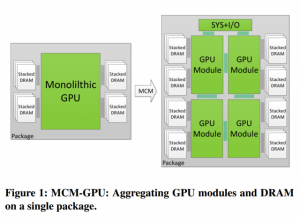
Several times, AMD together with Nvidia had used various cores in providing support for the extra monitors or to bond links between PCI Express and AGP. Nvidia has now been appraising the option of a multi-chip GPU which would interconnect with the other parts of the core such as MCM – Multi-chip-Module, considering the core component of the GPU, that have been single-die matters for a long time.
However monolithic GPU designs tend to have issues from various problems. At first they could be reticle-busters, pushing the limits of what TSMC, GlobalFoundries or Samsung could construct into a single core. Harvesting good GPUs from the corrupt ones could escalate issues when the manufacturer tries to harvest good die as in the case of Nvidia and the GTX 970.
In-House Simulator
The system that they utilised in recovering parts for the GTX 970 also had an influence on the memory bandwidth of the GPUswhile accessing its last 512MB of RAM. If GPUs had been built in modules, and linked together on a common package, the subsequent chip could theoretically be huge and more powerful than any single card.
The research team of Nvidia utilised an in-house simulator in evaluating their designs and build two virtual GPUs comprising of 256 streaming multiprocessors -SMseach.
One was based on the present monolithic design while the other utilised an MCM design. In the study of the author, they were of the belief that they can exceedthe performance of the biggest construct able GPU by 44.5% and come within 10% of a monolithic GPU die which exceeds any product presently buildable at any foundry.
If this type of approach in a perfect situation could harvest amazing development in performance as well as power consumption together with TDP, one would not have the complete GPUs horsepower focused in a small space. Caution would be essential against jumping to conclusion.
Non-Uniform Memory Access – NUMA
The authors of the report have acknowledged that this would need software which was NUMA – Non-Uniform Memory Access, compatible. Moreover there would also be an inevitable performance hit while accessing data that is held in different GPU or sharing information over numerous cores.
These types of performance have already taken place when consumers try to deploy arrays of GPUs and the performance penalties are now considerablytougher than what they tend to be in an MCM.It is left to be seen what Nvidia would be doing for the next couple of generations.
However a move to MCM GPUs tends to be almost certain. The issue is which company would be getting there first. It is believed that AMD’s Navi GPU architecture off in the distance could be utilising an MCM GPU design also particularly since the AMD has the tech in place with Zen, at the moment.